Warfarin
Warfarin is used to prevent clotting. Outside of its use in humans, warfarin is used as a poison to kill nuisance animals including mice and rats. Patients are strongly advised to take warfarin exactly as prescribed. The drug is available as oral tablets as well as injections. The drug has been approved for treating heart and clotting diseases, as well as use in patients that have recently had heart valve replacements or irregular heartbeat.1
- 1 Warfarin. MedlinePlus. 2016. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682277.html
Warfarin is a member of the coumarins, a group of chemicals that prevents blood clot formation by inhibiting enzymes that recycle vitamin K to its active form. Vitamin K is needed to complete the reactions that lead to blood clot formation. When the active vitamin K in the treated individual is depleted, blood clot formation is inhibited. Warfarin acts by decreasing the clotting ability of blood.1
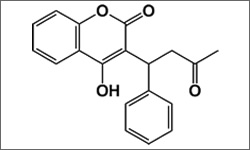
The structure above shows the 3D conformer Warfarin.
- 1 Warfarin. MedlinePlus. 2016. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682277.html
Warfarin can cause severe, even fatal, bleeding. Other severe side effects can be indicated by difficulty breathing, chest pain, nausea, swelling of the hands, feet, ankles or lower legs, vomiting or diarrhea. Other side effects include chills, changes in taste, feeling cold, gas, feeling tired, hair loss and pale skin. Warfarin can also cause the death of skin or other body tissues (gangrene). It is important that any patient suffering from side effects of warfarin contact their care giver right away.1
- 1 Warfarin. MedlinePlus. 2016. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682277.html
Due to increased bleeding risks, patients with a history of blood/bleeding disorders should consult their doctor before using warfarin. The drug is not recommended for patients who are pregnant or may become pregnant, because the drug can pass from mother to child. There have also been some reports of birth defects in children whose mothers were treated with warfarin while pregnant. Patients are advised against sports with high risks of physical injury as this may increase risk of bleeding. Patients are advised to consult a doctor before any changes in their normal diet. Doctors should also be aware of all medications, vitamins and supplements that the patient is taking because they could have negative interactions with the drug.1
- 1 Warfarin. MedlinePlus. 2016. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682277.html
