Bortezomib
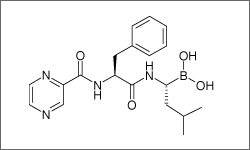
Bortezomib ia administered intravenously and subcutaneously, where around 80% of the drug binds to plasma proteins in the body. Bortezomib is approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma.1
- 1Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Bortezomib (VELCADE®) is rapidly taken up by body cells, and proteasome inhibition depends on the dose given. Inhibition is completely reversible, and levels of the drug must be allowed to return to baseline before a second administration. As long as the levels are allowed to return to baseline, there is no drug resistance after exposure. 1
The diagram below shows the 3D molecular structure of Bortezomib.
- 1Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Common side effects include: fatigue and weakness, nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, constipation, lowered blood cell count, nerve pain and vomiting. However, these symptoms frequently decrease with more cycles of treatment. Women should not become pregnant while taking this medication as it may cause damage to the unborn child. Blood tests should be performed often to monitor any decrease in cell counts. 1
- 1Velcade.. Prescribing Information. Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. July, 2016. [http://www.velcade.com]
